Allion Labs / Greg Tsai
Active Noise Cancellation (ANC) History
Active Noise Cancellation is a technology that utilizes speakers to produce sound waves with the opposite phase to nullify the noise it’s attempting to cancel.
ANC headphones play a pivotal role in communication products. In 1936, Paul Leug proposed an ANC patent in the US. In 1955, the research on ANC headphones began to rise. In 1989, Bose launched the first ANC headphones. In modern days, with the popularity of True Wireless Stereo (TWS) earphones, Apple added ANC functionality to the Apple AirPods Pro in 2019, officially bringing ANC earphones into the public eye.
Noise Control Analysis
The specific model did not conform to CEC standards, causing the TV to have no response when the soundbar was turned on.
Noise reduction scenarios can be divided into three different categories, depending on the communication system.
1. Eliminating background noise on the “Calling End”

The purpose is to ensure the signal being sent over is clean. The beneficiary of this is the receiver of the signal.
The following can be applied in this situation:
- Directional microphones
- Array microphones
- Bone conduction microphones or in-ear microphones
- Speech separation algorithms
2. Eliminating the noise at the “Receiving End” which was mixed with the signal from the “Calling End”

This type of noise cancellation mainly benefits the receiver, eliminating the excess noise mixed in with the signal at the calling end. The intended sound signal and excess noise have been mixed, so the only solution is to separate them through software algorithms.
The following can be applied in this situation:
- Speech separation algorithms
3. Eliminating background noise at the “Receiving End”
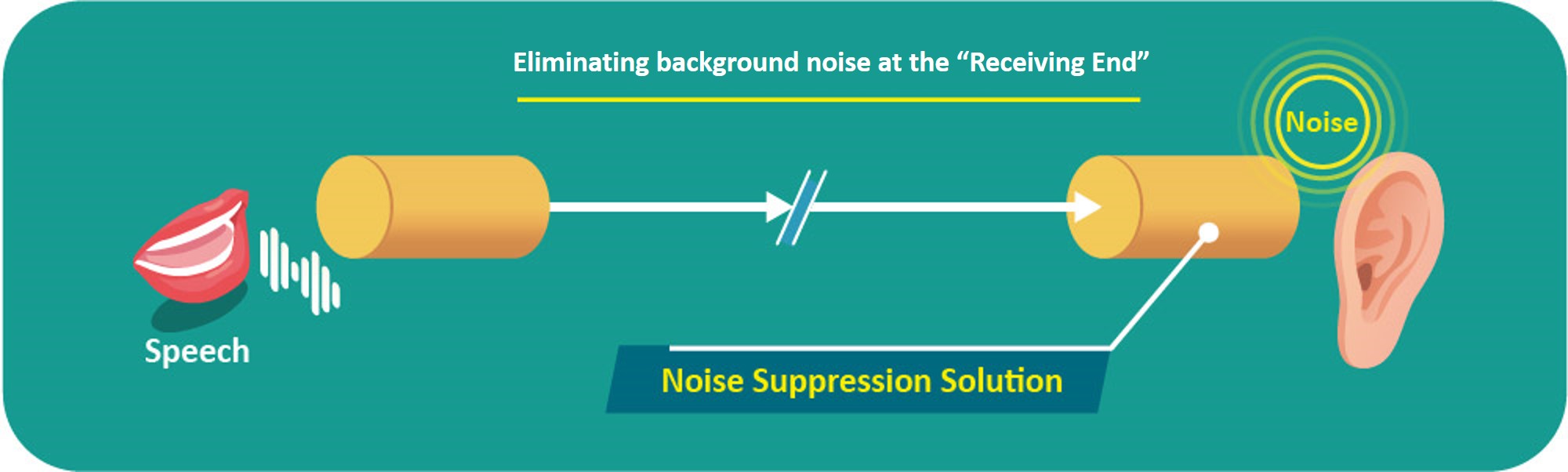
This type of noise cancellation benefits the receiver, allowing them to hear the sound signal from the calling end without interference from their environment.
The following can be applied in this situation:
- Passive noise isolation (acoustic noise isolation)
- Active noise control (noise cancellation with anti-noise)
A good noise cancellation solution should include these three types of technologies simultaneously, as shown below.
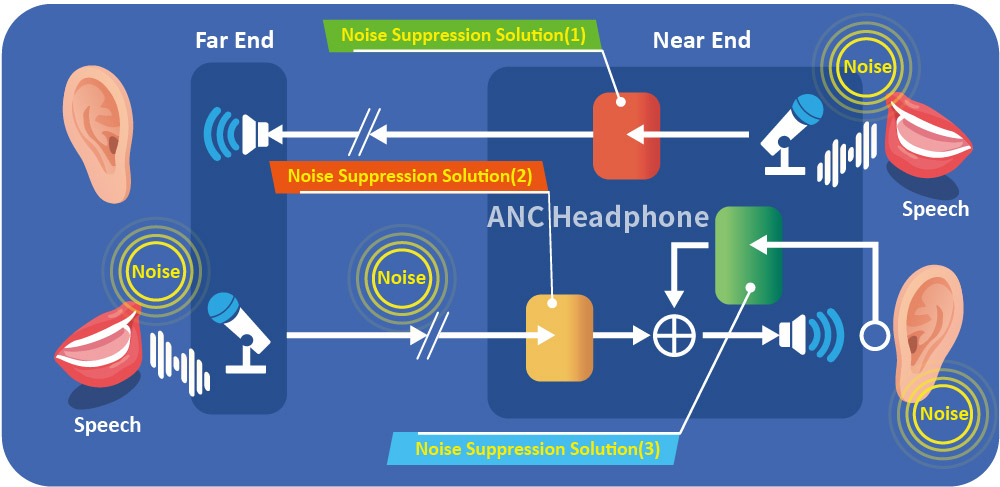
The following goals can be achieved:
- Prevents noise from the calling end from being transmitted over
- Enables the receiving end to remove excess noise created from the calling end and the transmission
- Suppresses background noise at the receiving end, allowing the receiver to hear clearly
Most ANC headphones available on the market today only include the third type of noise reduction mentioned above. Therefore, this article will mainly focus on discussing ANC technology.
Active Noise Cancellation Fundamentals
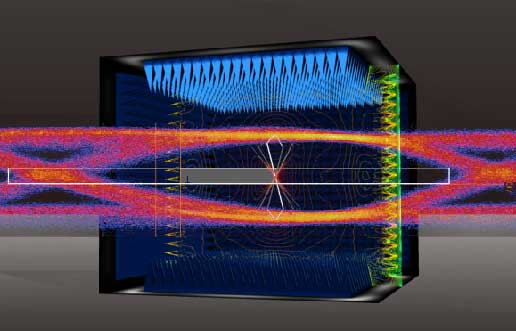
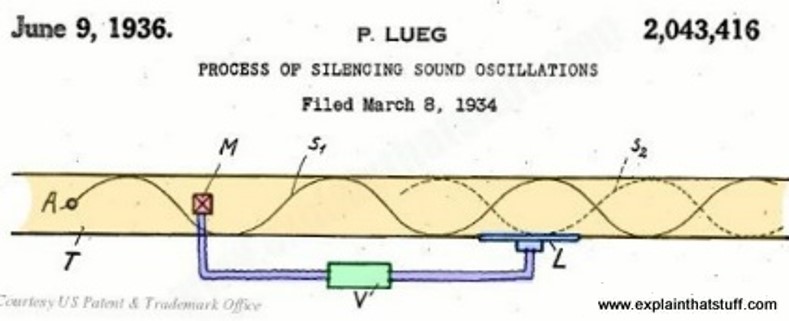
The earliest ANC noise cancellation technology was introduced when a US patent was proposed by Paul Lueg in 1936, applying noise reduction to pipelines. The patent map is shown below.
Let’s take a look at how sound waves travel in a pipe. When the piston moves forward, air particles are compressed, and the air pressure of the area will increase. As the piston moves back, the air pressure will decrease. This becomes a cycle that repeats. In the red dots, you can observe the waveforms and pressure changes as time moves on.
Find more details about sound waves here.
https://resource.isvr.soton.ac.uk/spcg/tutorial/tutorial/Tutorial_files/Web-basics-sound.htm
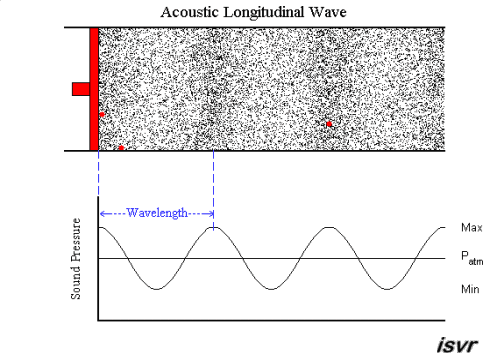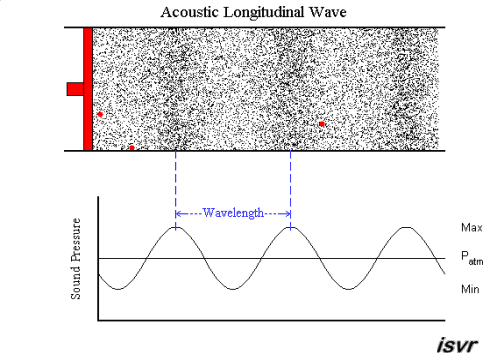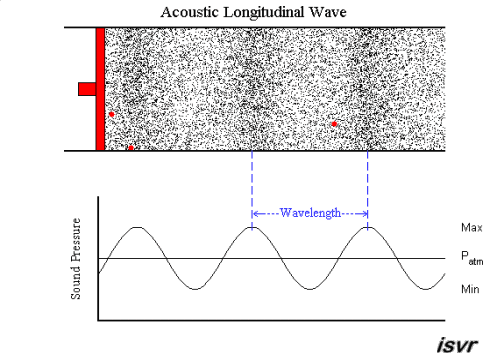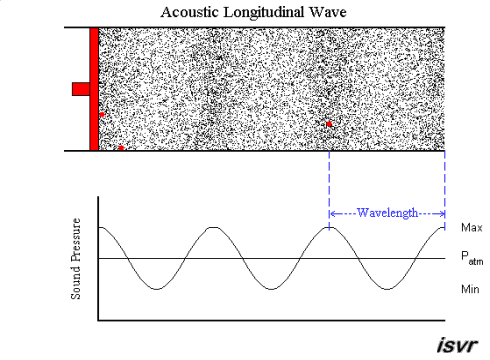
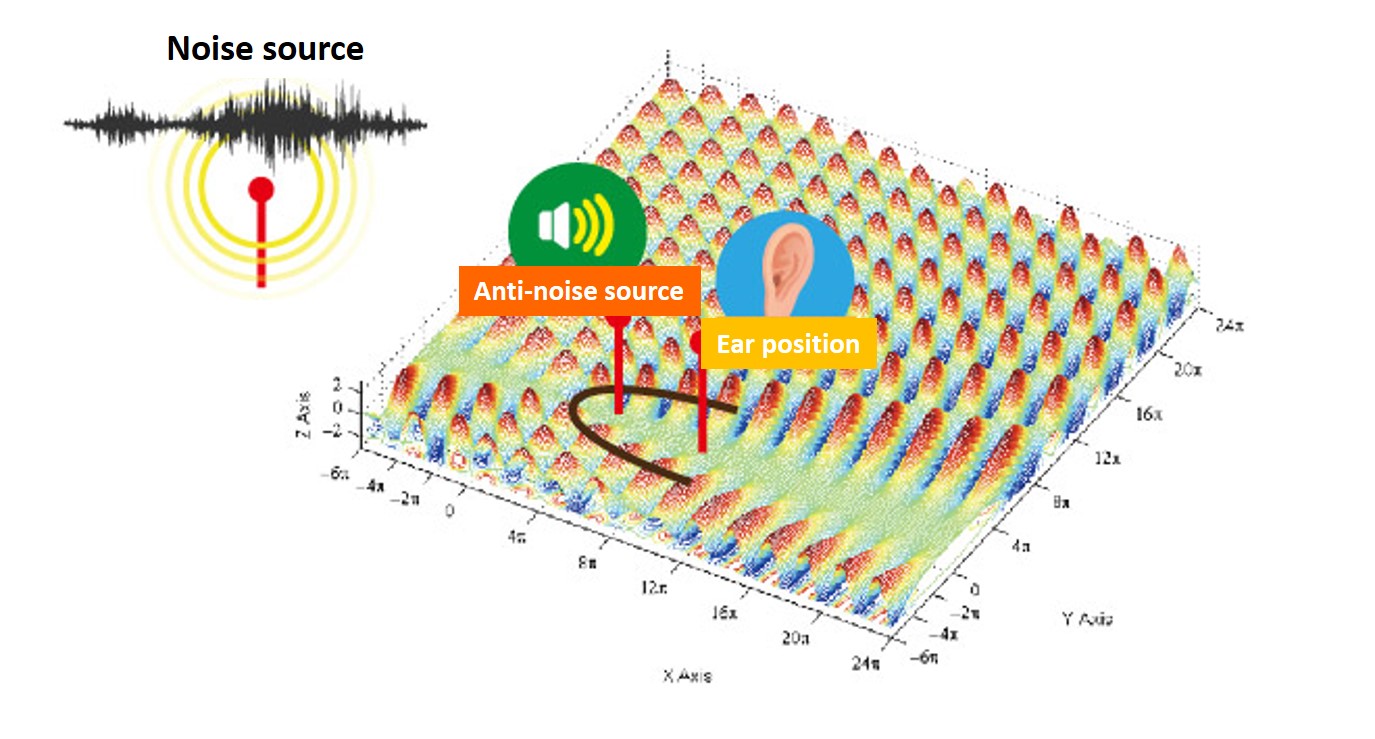
Paul Lueg’s idea was to install a microphone in the pipeline to record the sound pressure of the upper pipeline and simultaneously emit the same volume but opposite-phase sound waves from the lower pipeline, attempting to eliminate the noise from the lower pipeline. This phenomenon is illustrated in the figure below.
This phenomenon is called a dipole, which is a sound field formed by two sound sources with opposite phases. In the central area, a destructive wave is generated due to the opposite phase of both waves, leaving the sound pressure to be zero.

If noise cancellation products want to achieve active noise reduction, they must be appropriately designed. The basic concept of noise-cancelling headphones is shown in the figure below.
Usually, active noise reduction cannot exist independently. It’s usually combined with passive noise isolation technology for a better effect, as shown below.
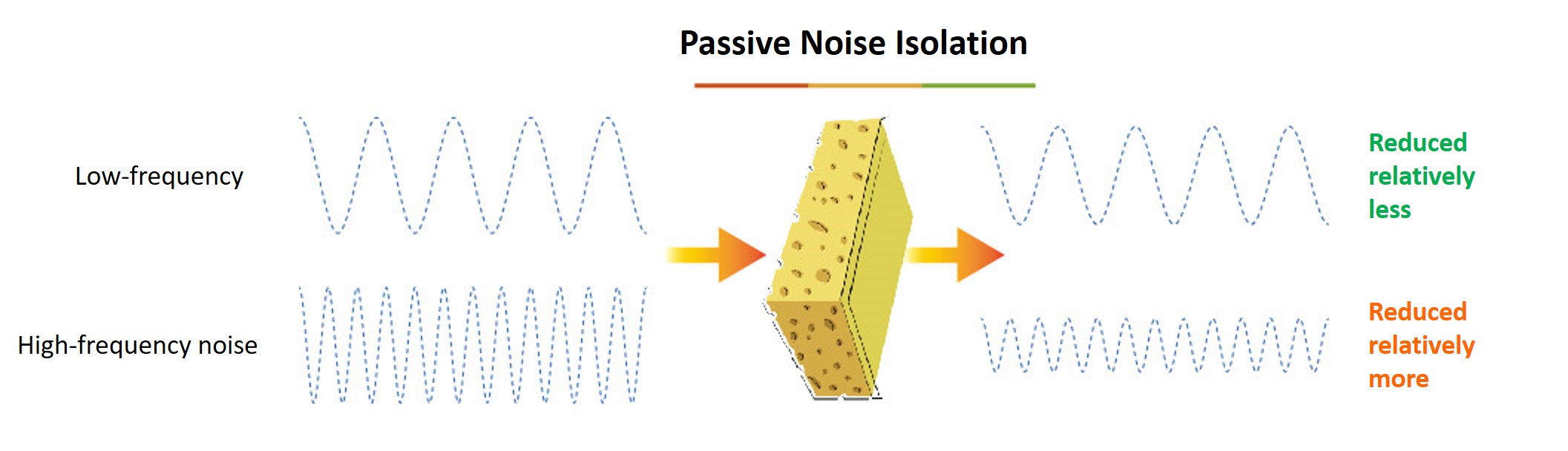
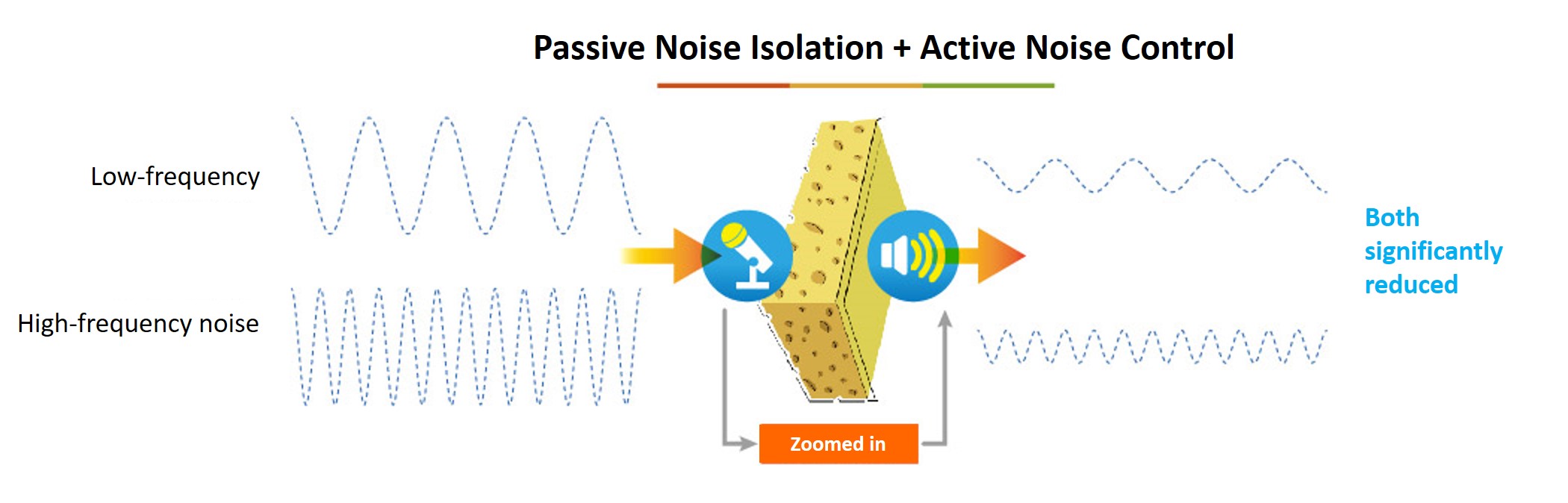
Passive noise isolation mainly relies on the material it’s made from, usually having a better effect on high frequencies. If passive noise isolation was used for low frequencies, the material required would be very large in volume. Active noise control can handle lower frequencies better due to destructive interference. Passive noise isolation and active noise control are complementary to one another.
When discussing noise reduction and sound isolation performance in ANC headphones, both passive sound isolation and active noise reduction levels must be taken into consideration.
Allion’s Noise Cancelling Headphones Testing Setup
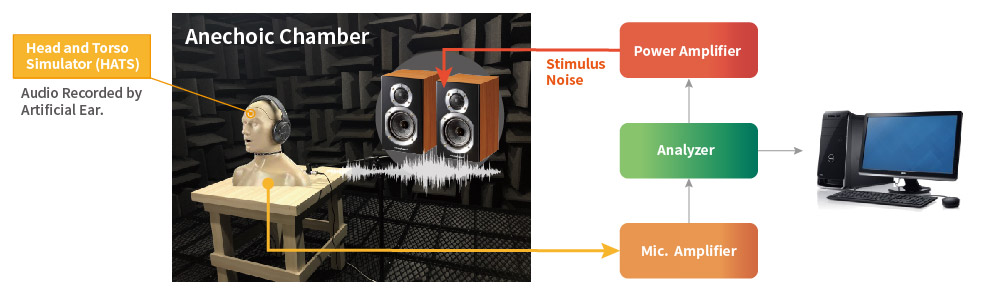
To evaluate the performance of noise-cancelling headphones, the DUT is placed on a head and torso simulator (HATS). The volume is measured before and after the noise reduction through an artificial ear to evaluate noise reduction (calculating insertion loss).

The testing setup
Noise cancellation performance was evaluated under the following conditions:
- Performance was measured in the artificial ear when no headphones were worn.
- Performance was measured with non-ANC headphones worn (measuring passive noise isolation).
- Performance was measured with ANC headphones worn
Subtract the first test results from the second to get passive noise isolation performance, and subtract the second test results from the third to get active noise control performance.
Results
The following figure shows the test results of the Logitech ZoneWireless headset:
Test 1
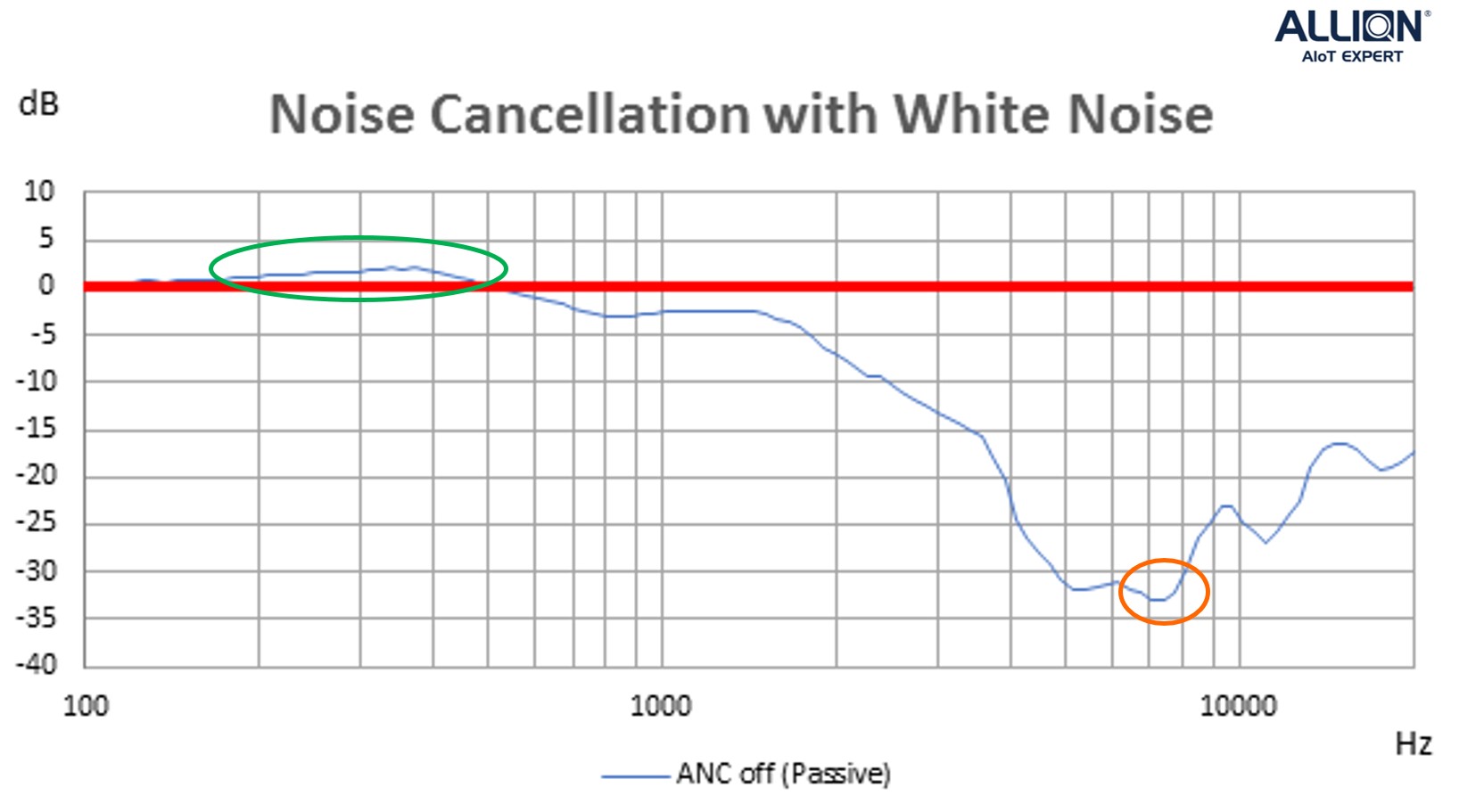
Figure 1 shows the performance of passive noise isolation. It can be seen that noise isolation is better for higher frequencies. The attenuation goes above 6dB at 2kHz, and t rises to 33dB at 7kHz (the orange circle). However, passive noise isolation is not as effective for lower frequencies, even having the volume increase (the green circle).
Test 2
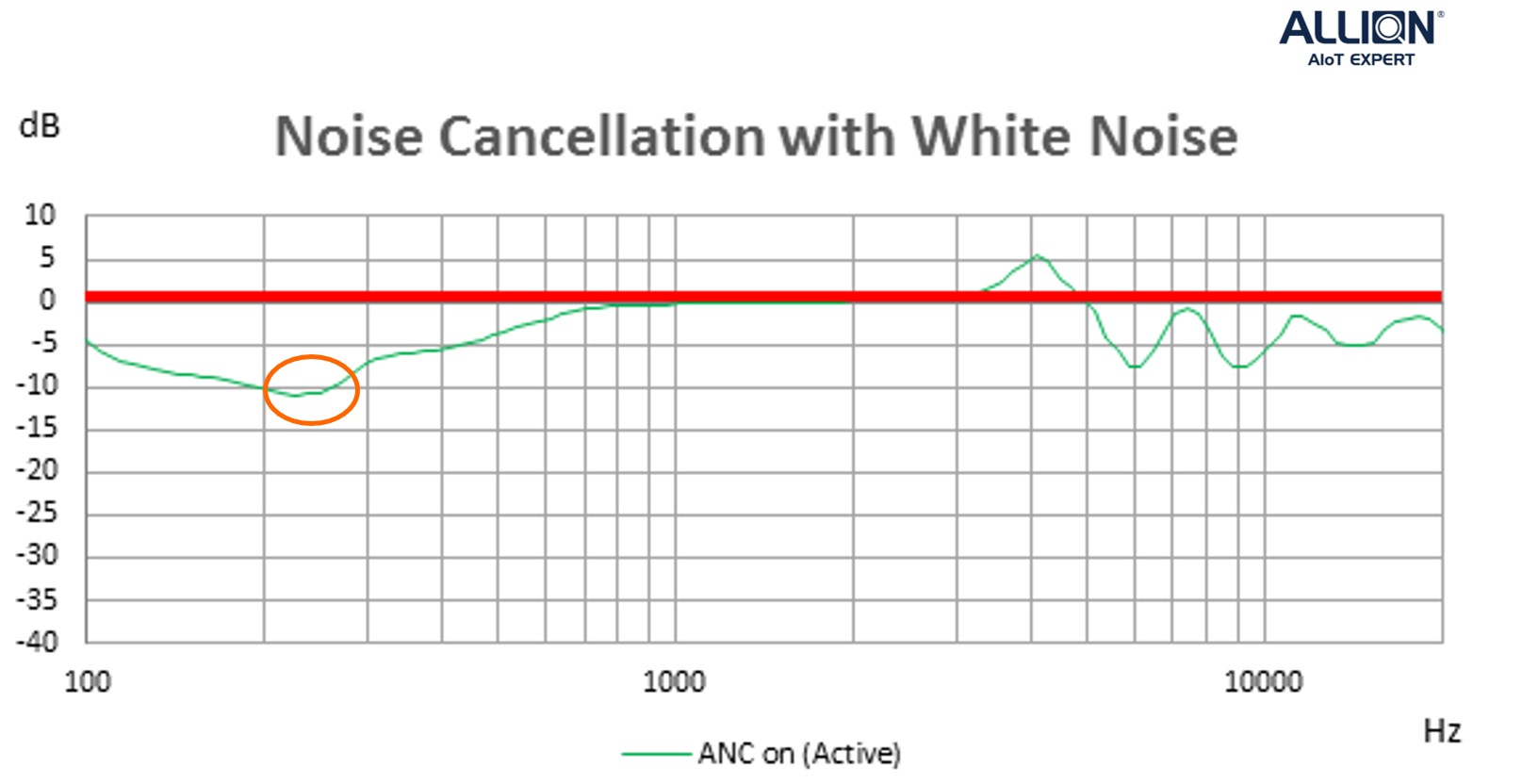
Figure 2 shows the performance of active noise control. It can be seen that it primarily focuses on low-frequency noise reduction. For this product, there is more than 2dB attenuation below 600Hz, and around -10 dB attenuation around 230Hz (the orange circle).
Test 3
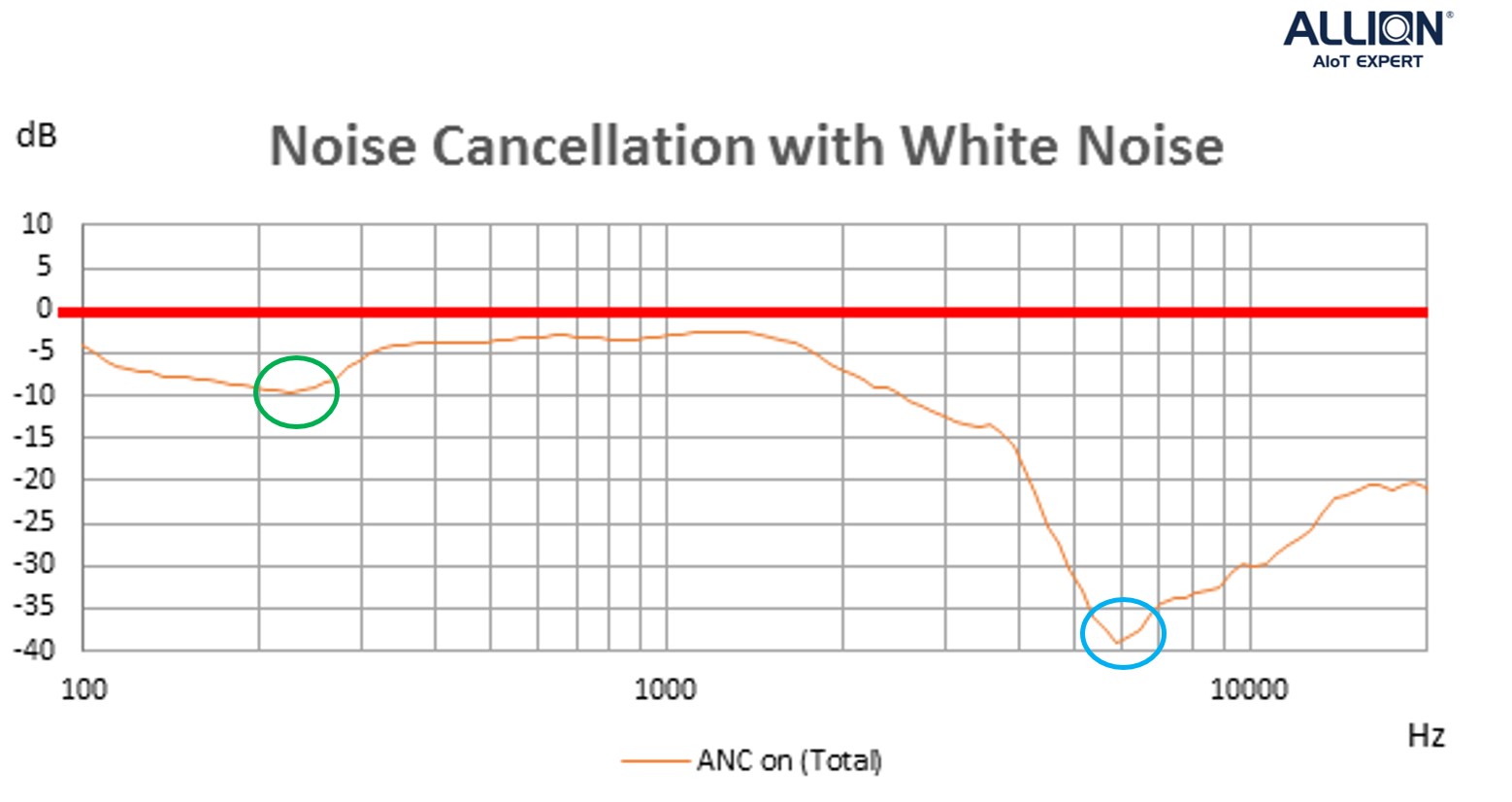
Figure 3 shows total noise reduction with ANC turned on. It can be seen that the low frequencies have a noise reduction effect of around 10dB at 230Hz (the green circle) and around 39dB at 6kHz (the blue circle).
Facing the growing demand for wireless headphones, how can manufacturers plan and take advantage of ANC-related business opportunities?
n addition to sound quality, noise filtering is crucial for the user experience. Noise reduction has now become one of the main indicators that influence consumers to make a purchase. This is one of the reasons why manufacturers are so interested in ANC-related products and business opportunities.
Allion has experienced teams with professional testing equipment and laboratories dedicated to our clients. We can provide customized testing solutions that help you advance in your industry.
If you have any questions, please feel free to contact us through the online form.