Voice recognition has become the prevalent technology for remote authentication. To fulfill people’s needs for convenience, tech giants such as Amazon, Google, and Apple started to develop their own voice recognition systems and have invented and brought the smart assistant to the market.
Generally, a smart assistant can be vocally activated to provide entertainment support (e.g. music and radio), help search information (e.g. wiki, translation, and recipe), and control other smart devices in houses, offices, or hotel rooms. These clever helpers later become the focus for those manufacturers who attempt to step further in the IoT era. For example, Jingdong’s smart assistant, Dingdong, was launched in 2016, and Xiaomi and Alibaba also launched XiaoAi and Tmall Gani in 2017. The market competition of smart assistants, consequently, has been led into the white-hot stage.
With powerful capabilities, however, comes with complex product validation methods. Allion’s experts, based on their extensive testing experience, decided to research and have categorized the three most frequent issues of smart assistants, including misinterpretation, high recognition failures in application, and wireless signal interference. They later operated trial cases to verify these issues on the various smart assistants in the market. In this article, we argue that, a positive user experience for a smart device involves not only in the product itself but in its diverse applications. First, we will explain the three issues by sharing the results from our smart assistant trial cases. Then we will introduce Allion’s test solutions for smart assistant.
The Most Frequent Issues in Smart Assistant Application
#1 Misinterpretation
People often need time to familiar with the distribution of the area, such as the locations of light and a/c system switches, when first stepping into a room. By establishing smart assistants as “control hubs” of all the electronic equipment, individuals can soon be able to turn on lights and radio or change TV channels vocally. However, some of the requests were often led to incorrect orders since voice assistants could pick up wrong key words or misunderstand the conversations.

In one of our trial cases, we asked the voice assistant to turn off the air purifier in 3 minutes. Nevertheless, as the illustration shown above, the DUTs (Device under Test) could fail to pick up the keywords, “3 minutes,” and thus responded and turned off the air purifier right away. According to our test results, misinterpretation issues were frequently occurred even for those sentences defined by the product spec, and these faults could decrease user satisfaction significantly.
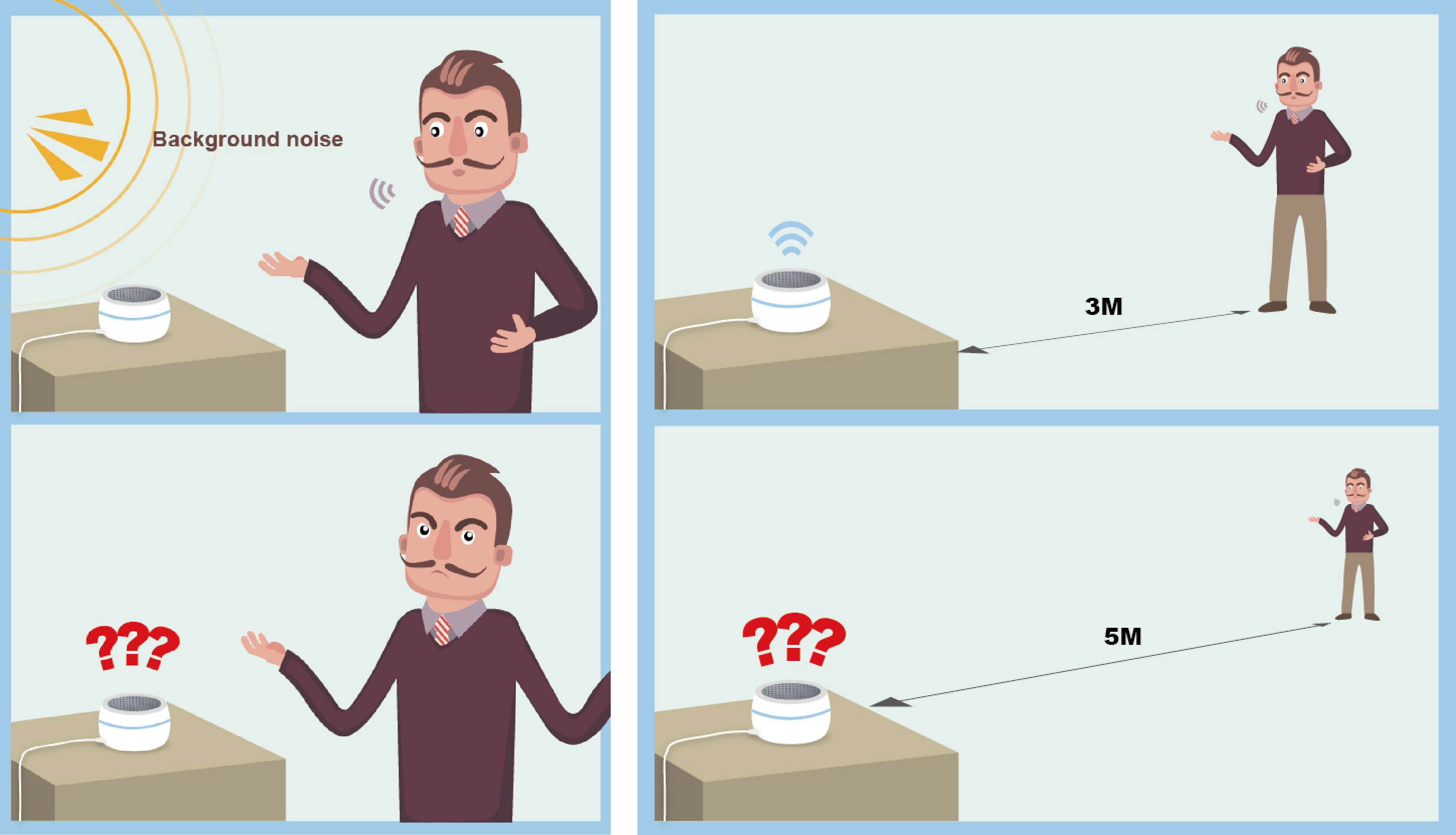
#2 High Recognition Failures in Application
Besides misinterpretation issues, the speech recognition capability of smart assistant can significantly affected by environmental factors, such as background noises or the distance between the user and DUT. To be more specific, we found the DUTs had uneven awakening success rate while testing them under the environment with 30 dB and 50 dB noise level. We also found some of the smart assistants were hardly woken up if the distance between the user and the DUT was over 5 meters. Since the user environments of smart assistants are always complicated, the effects of environmental factors should become one of the indicators when validating the recognition capability of smart assistants.

#3 Wireless Signal Interference
In addition to the physical environmental factors (e.g. noise and distance) mentioned above, the invisible wireless signals in the environment can bring negative effects for the performance of smart assistants. Since most of the IoT devices use 2.4 GHz wireless technologies (e.g. Wi-Fi, Bluetooth®, Zigbee, etc.) to go on-line, co-channel/adjacent interference could be occurred in this congested frequency band.
In our trial cases, the rate of response latency was increased when we created multiple wireless signals (i.e. those technologies use 2.4 GHz) in the same roof, even though all the devices showed full bars of wireless signals. However, the DUTs could, again, perform normally once we remove all the disturbances in the area.

Allion Test Solutions for Smart Assistant
Aiming to help product makers discover and solve issues before launching them to the market, Allion has proposed a solution package for smart assistants. This package is separated into two parts: Product Validation and User Scenario Simulation.
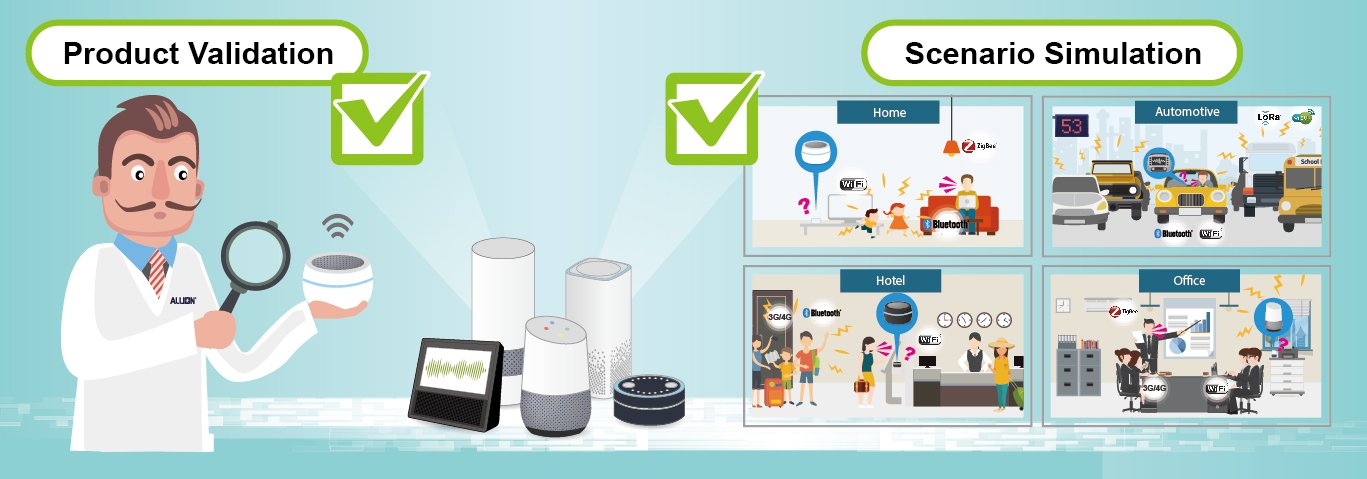
Product Validation
In product validation aspect, we help manufacturers fully validate the basic function, interoperability, and acoustic performance of smart assistants. Not only do we operate functionality test, which include key feature, user interface, and awakening success rate validation, but our experts also validate the interoperability by pairing up the DUTs with the devices in Allion’s device library, which contains thousands of APs, mobile phones, and IoT devices.
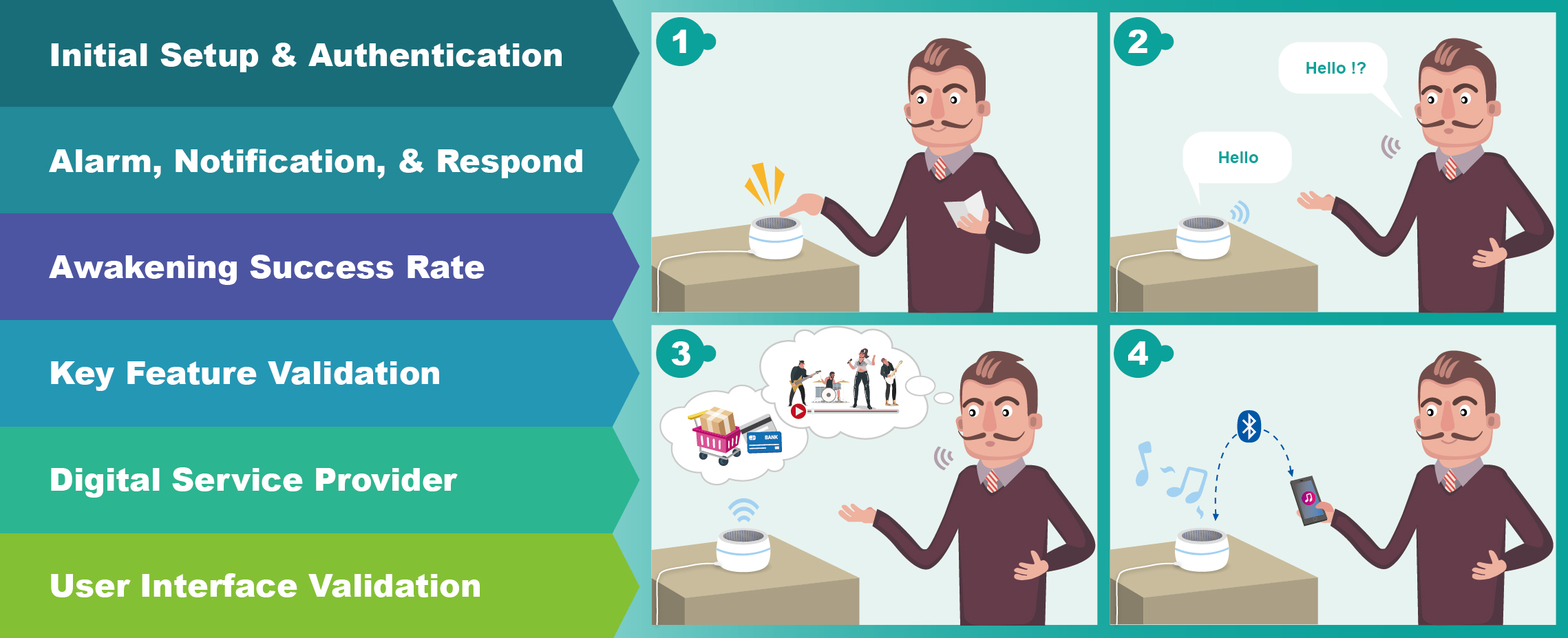
Part of the Test Items in Allion’s Functionality Test

Allion’s Device Library
For the acoustic performance of smart assistants, our experts can formulate customized testing plans. Based on the product’s market position, we will help you define and manipulate key variables, such as the azimuth, angle, distance, and decibel of noises, and test your devices with our superior equipment and test facilities.
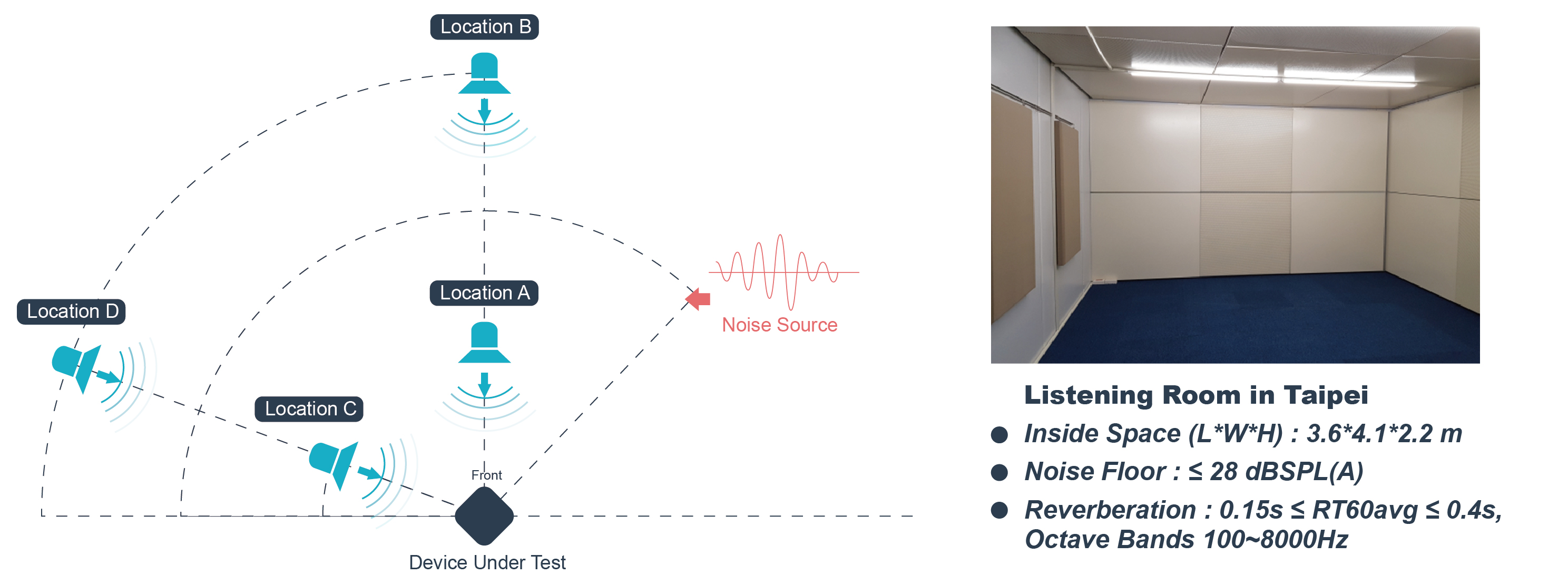
User Scenario Simulation
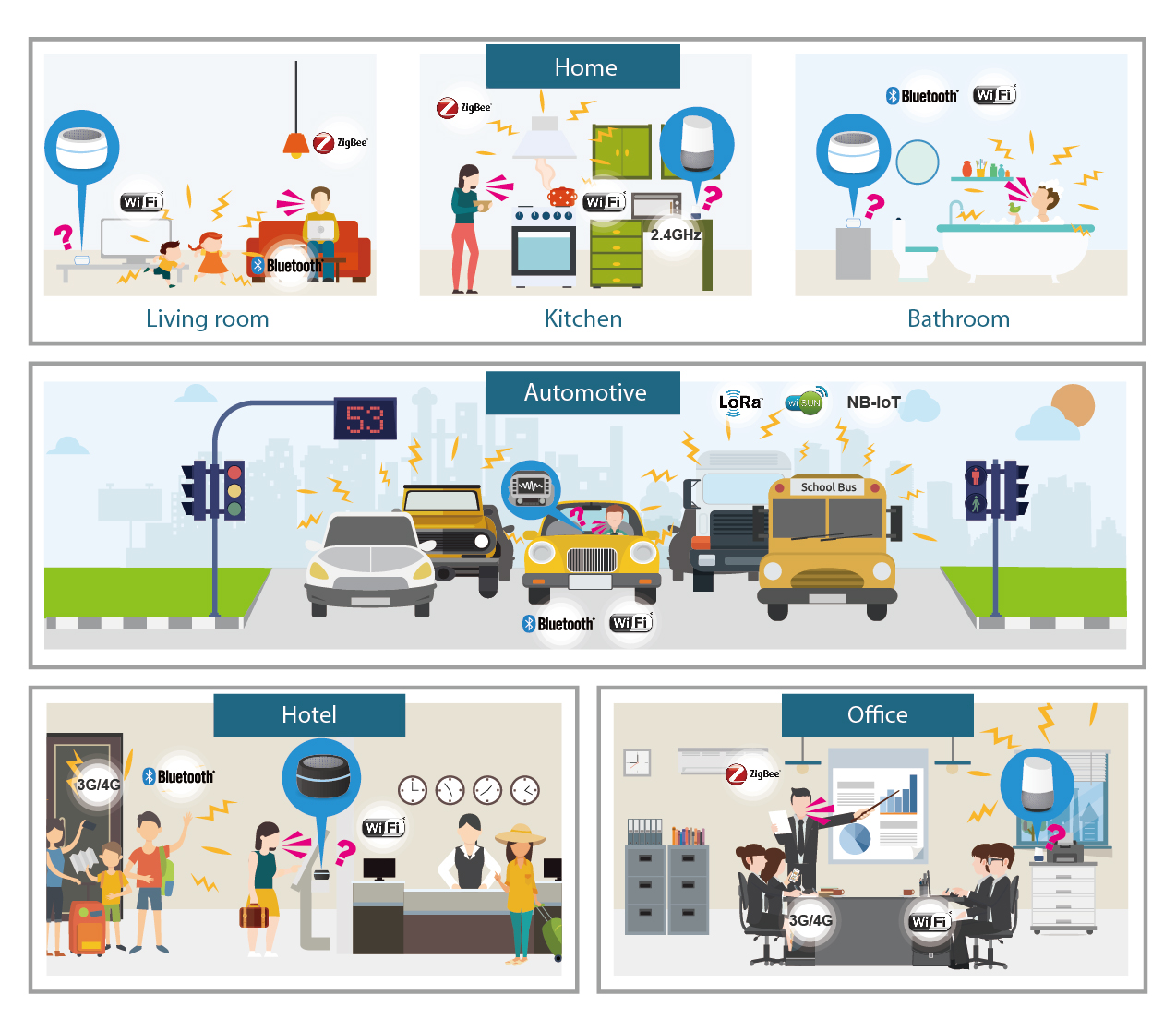
As we mentioned previously, the diverse application of smart assistant has complicated its validation method. Therefore, we propose user scenario simulation to help vendors test their products under different conditions. For example, in home scenario, we built living room, bathroom, and kitchen models and created possible challenges (e.g. children screaming, cooking or water noises, and complex wireless ecosystem) to test whether the DUTs, especially those have passed the product validation tests, can retain their performance. The illustration below shows various scenarios that we are developing.
To validate the wireless condition in the customized scenarios, we have developed Heat Map Analysis to visualize the wireless distribution of the environment. By perceiving Received Signal Strength Indicator (RSSI), our experts can identify root-cause and assist clients further improve the connectivity of their products via the specialized RF debugging support.
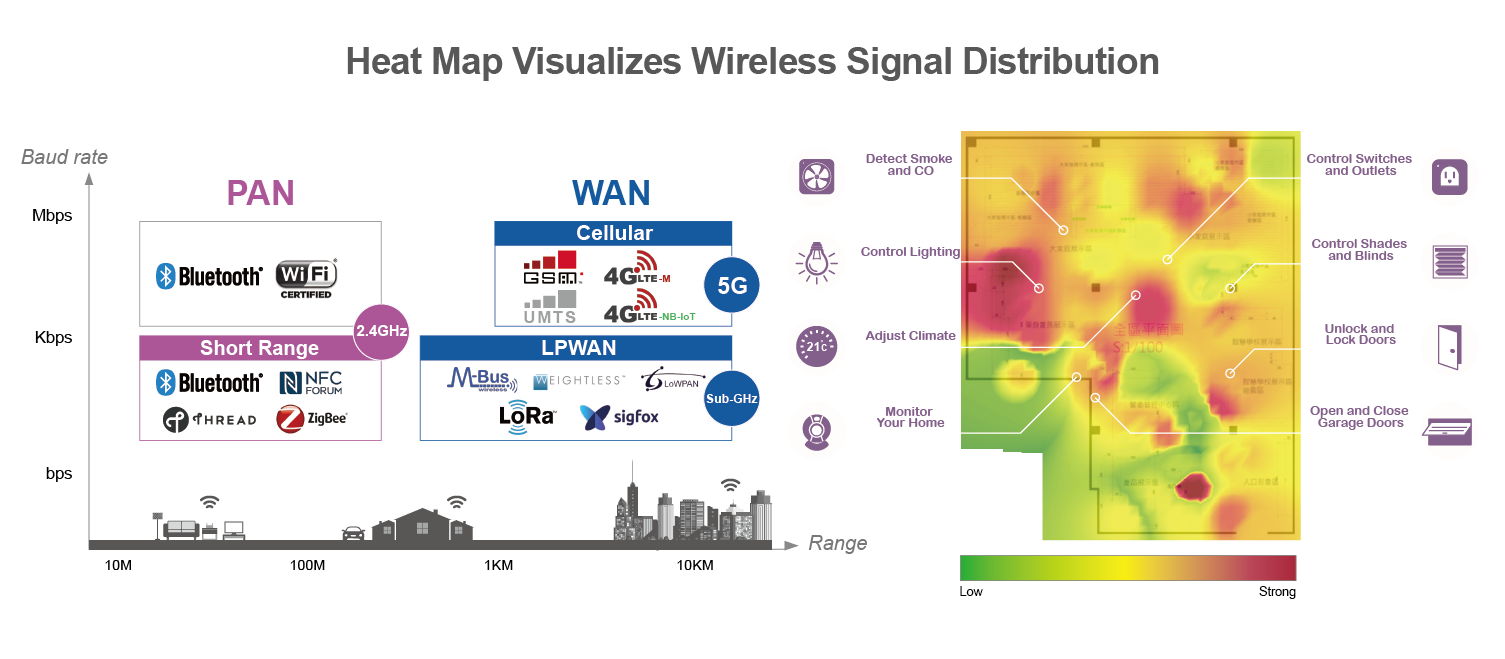 *To know more about Heat Map, please read Validate your Smart Device with Real World Factors: Allion’s Heat Map Analysis Program.
*To know more about Heat Map, please read Validate your Smart Device with Real World Factors: Allion’s Heat Map Analysis Program.
Conclusion
In conclusion, we have explained the three most frequent issues by sharing the results from our smart assistant trial cases, including misinterpretation, high recognition failures in application, and wireless signal interference. Nevertheless, there are far more issues that are waited to be categorized from the diversified application. We thus proposed a test solution package for smart assistant, aiming to help our client launch better products to the world.
As we claimed at the beginning, a positive user experience for a smart device involves not only in the product itself but in its diverse applications. Therefore, we will keep researching and inventing new test methodologies for all the IoT products in the market. In the next article, we will share and specifically discuss the test results from our interoperability trial cases for smart assistants.
Please contact us if you are interested in any of our service